The history of ancient India is rich, diverse, and filled with complexities. Over time, various theories have been proposed to explain the formation and development of early Indian civilization. One of the most controversial and debated ideas in this context is the Aryan Invasion Theory. This theory suggests that a group of nomadic, warrior-like people called the Aryans migrated into the Indian subcontinent around 1500 BCE and played a significant role in shaping the history and culture of ancient India. In this article, we will explore what the Aryan Invasion Theory is, its impact on our understanding of ancient Indian history, and how it has shaped modern interpretations of Indian society.
What is the Aryan Invasion Theory?
The Aryan Invasion Theory suggests that around 1500 BCE, a group of Indo-European speaking people, known as the Aryans, migrated into India from the steppes of Central Asia, specifically from areas around the Caspian Sea and modern-day Iran. According to this theory, the Aryans invaded and conquered the indigenous people of the Indian subcontinent, leading to significant cultural, social, and religious changes.
The primary sources that support this theory come from the Vedas, the ancient religious texts of Hinduism. The Rigveda, the oldest of the four Vedas, describes the arrival of a group of people called the “Aryas” (noble ones), who fought battles, defeated local tribes, and established their own rule in northern India. The Vedas mention the use of chariots and advanced weaponry, which suggested a different level of technology compared to the indigenous people of India at the time.
The theory gained prominence during the colonial period in the 19th and early 20th centuries, particularly with the works of European scholars and historians. The British colonial rulers in India, for example, used this theory to justify their dominance by portraying the Aryans as superior conquerors who brought civilization to the subcontinent.
Impact of the Aryan Invasion Theory on Indian History
The Aryan Invasion Theory has played a crucial role in shaping our understanding of ancient Indian history. For many years, this theory was widely accepted by historians, and it became a dominant narrative in textbooks and academic discussions. However, its influence is not limited to the academic sphere; it also had a significant cultural impact, influencing the way Indian history was perceived both in India and abroad.
- Reinforcement of Colonial Narratives: During British colonial rule, the Aryan Invasion Theory was used to strengthen the idea that India needed to be ruled by a foreign power for its own good. By portraying the Aryans as a foreign, superior group who brought civilization to the indigenous people, British scholars suggested that India’s history was marked by a constant struggle between invaders and the native population. This narrative helped justify colonial control over India by portraying the British as the inheritors of the Aryan legacy, bringing progress and order to a chaotic and backward land.
- Impact on Indian Nationalism: The Aryan Invasion Theory also had a profound impact on the development of Indian nationalism. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Indian leaders and intellectuals began to resist the colonial narrative and sought to reclaim their ancient heritage. Some nationalists rejected the idea that the Aryans were invaders and instead promoted the idea that the Aryans were indigenous to India. This was a way to assert the pride and self-worth of the Indian people, countering the colonial notion that India had always been a land of invasions and foreign rulers.
- Cultural Identity and Historical Debate: The debate around the Aryan Invasion Theory has also played a significant role in shaping India’s cultural identity. Some scholars and communities have identified themselves with the ancient Aryan culture, while others see the theory as an attempt to erase the history of the indigenous people of India. The idea of Aryan identity has also been linked to issues of caste and social divisions, as the early Aryans were often associated with the upper classes in later Hindu society. Thus, the Aryan Invasion Theory has been a key factor in the development of ideas about race, ethnicity, and social hierarchy in India.
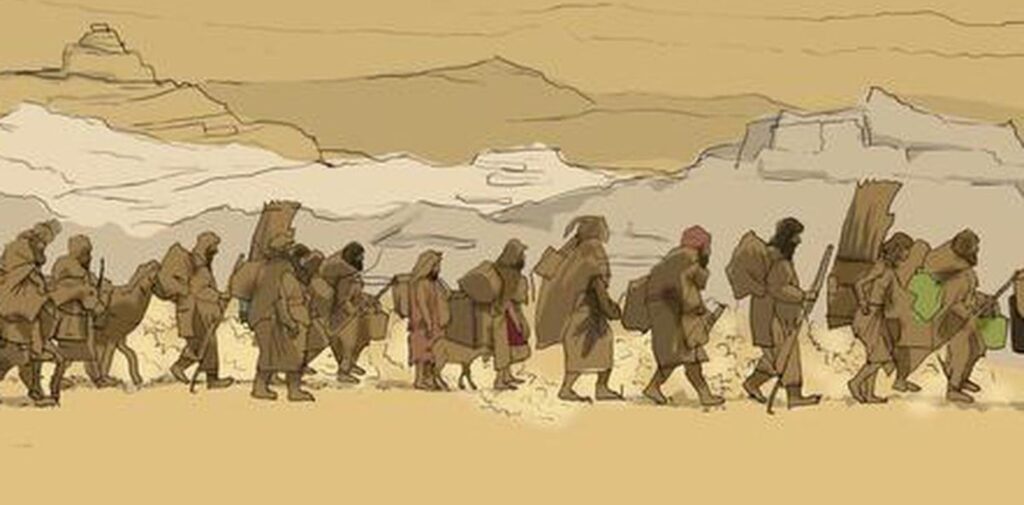

Challenges to the Aryan Invasion Theory
While the Aryan Invasion Theory had a lasting influence, it has faced significant challenges in recent decades. Modern archaeology, genetics, and linguistic research have questioned many aspects of the theory, leading scholars to reconsider its accuracy.
- Archaeological Evidence: One of the main challenges to the Aryan Invasion Theory comes from archaeological evidence. Excavations of ancient sites such as Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro, which are part of the Indus Valley Civilization, show no signs of invasion or destruction around the time the Aryans were believed to have arrived. The cities of the Indus Valley were well-planned and sophisticated, with no evidence of external violence or military conquest. Instead, the decline of the Indus Valley Civilization is believed to have been caused by factors such as climate change, river shifts, or internal social issues. This suggests that the collapse of the Indus Valley Civilization was not the result of an invasion by Aryan forces.
- Genetic Studies: Advances in genetic research have also cast doubt on the Aryan Invasion Theory. Studies of the genetic makeup of modern populations in India show that the people of the subcontinent share a common genetic heritage, with little evidence of a large-scale migration from outside the region. Genetic data suggests that the Indian population has been relatively stable over thousands of years, with gradual mixing and blending of different groups rather than the sudden influx of foreign invaders. This challenges the idea that the Aryans were a distinct, invading group.
- Linguistic Evidence: Linguistic studies of the Indo-European language family have also raised questions about the Aryan Invasion Theory. While it is true that the languages spoken in northern India belong to the Indo-European family, which is believed to have originated in Central Asia, there is no clear evidence that these languages arrived through violent invasion. Instead, it is more likely that the spread of these languages was part of a gradual cultural and linguistic diffusion, rather than an aggressive military conquest.
- Theories of Migration and Assimilation: In recent years, many scholars have moved away from the idea of an “invasion” and instead propose a theory of migration and assimilation. According to this view, the Aryans may have migrated into India over a long period of time, peacefully mixing with the indigenous population rather than conquering them. This theory suggests that the spread of Indo-European languages and culture in India was a complex, gradual process that involved both migration and cultural exchange.

The Legacy of the Aryan Invasion Theory
Despite the challenges to the Aryan Invasion Theory, it has left a lasting legacy on the study of ancient Indian history. It influenced the way historians, archaeologists, and scholars approached the history of India for many decades. The theory also played a key role in shaping cultural and political discussions in India, particularly in relation to issues of race, identity, and social hierarchy.
Today, while the Aryan Invasion Theory is no longer accepted as a simple explanation for the history of ancient India, it continues to influence how people understand India’s past. The debate over the theory highlights the complexities of interpreting history and the ways in which ideas about race, identity, and power shape our understanding of the ancient world.
Conclusion
The Aryan Invasion Theory has been one of the most influential and debated ideas in the study of ancient Indian history. While the theory has been challenged by modern archaeological, genetic, and linguistic research, its impact on the way India’s past is understood cannot be underestimated. The theory played a significant role in shaping colonial narratives, national identity, and the cultural debates that continue to shape India today. As new evidence and perspectives emerge, our understanding of ancient India continues to evolve, offering a more nuanced and complex view of this fascinating civilization.


