The struggle for Indian independence was shaped by numerous global events and ideologies that inspired and influenced Indian nationalists. One such pivotal event was the American Revolution (1775-1783), which resulted in the thirteen American colonies gaining independence from Britain. The ideals and outcomes of the American Revolution had a profound impact on Indian nationalists, helping shape their thinking and strategies in their own struggle for freedom.
In this article, we will explore the influence of the American Revolution on Indian nationalists, focusing on the key principles that resonated with Indian thinkers and leaders. We will also examine how these ideals were adapted and applied to the Indian context during the fight for independence.
The American Revolution: A Prelude to Change
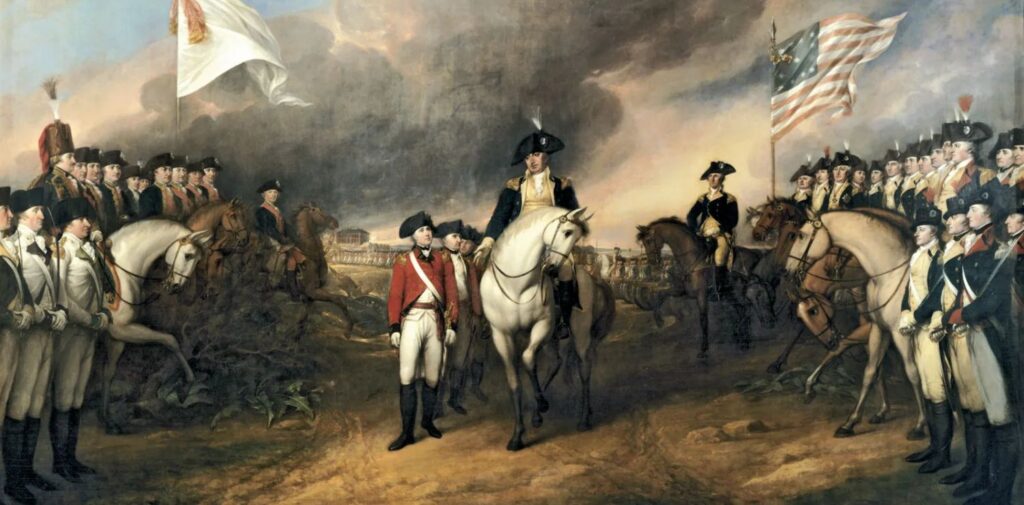
The American Revolution was a significant moment in history, as it was one of the first successful revolutions against a colonial power. It was driven by a desire for independence, self-governance, and the protection of natural rights. The American colonies, under British rule, were seeking to escape what they saw as unfair taxation and lack of political representation. The revolution culminated in the Declaration of Independence in 1776, which outlined the inherent rights of individuals to life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness.
This revolutionary movement was not just about breaking free from British control but also about establishing a new kind of government, one that was based on the principles of democracy, equality, and individual rights. These ideas resonated across the globe, and in India, they found a receptive audience among the intellectuals and freedom fighters who were beginning to question British colonial rule.

Key Principles of the American Revolution and Their Impact on Indian Nationalists
Several key principles from the American Revolution strongly influenced Indian nationalists. These ideas of liberty, equality, and self-governance were deeply inspiring and laid the foundation for a broader nationalist movement in India.
1. The Ideals of Freedom and Independence
At the core of the American Revolution was the belief that a nation had the right to determine its own future, free from external domination. The American colonists revolted against British rule because they wanted freedom and the ability to make decisions about their own governance. This spirit of independence resonated with Indian nationalists, who were similarly subjected to British colonial rule and denied self-governance.
Leaders like Lala Lajpat Rai, Bal Gangadhar Tilak, and Subhas Chandra Bose were influenced by the American idea that a people had the right to resist foreign domination and fight for their freedom. The idea of sovereignty—control over one’s own land and people—became central to India’s independence struggle. The American Revolution, by showing that it was possible to break free from a colonial power, gave Indian nationalists hope and conviction in their own struggle.
2. The Concept of Popular Sovereignty
One of the most important ideas from the American Revolution was that of popular sovereignty—the principle that the power to govern should lie with the people, not with a monarch or foreign ruler. The Declaration of Independence famously states that “governments are instituted among men, deriving their just powers from the consent of the governed.” This concept directly challenged the idea of imperial rule, where power was centralized in a foreign nation like Britain.
Indian nationalists, particularly those in the Indian National Congress (INC), began to embrace the idea of popular sovereignty as they pushed for a greater say in India’s governance. Leaders such as Jawaharlal Nehru and Mahatma Gandhi were inspired by this principle and worked toward achieving self-rule for India through democratic means. The American Revolution provided a model for how colonized peoples could assert their rights and demand the power to govern themselves.

3. The Importance of Equality and Justice
The American Revolution was also rooted in the belief in equality and justice for all citizens, regardless of their background. The American colonists were fighting against the unjust treatment of their society under British rule, particularly the issue of taxation without representation. This principle of equality and fairness appealed to Indian nationalists who were subject to British policies that discriminated against Indians in favor of the British.
Indian reformers like Raja Ram Mohan Roy and Swami Vivekananda were deeply influenced by the American emphasis on human dignity and equality. They sought to eradicate social inequalities within Indian society, including the caste system and the mistreatment of women, while also fighting against the discriminatory policies of British colonial rule. The American Revolution demonstrated that a government could be founded on the principles of equality, a notion that Indian nationalists sought to incorporate into their vision for an independent India.
4. The Revolution and Armed Struggle
While the Indian independence movement is often associated with nonviolent resistance, the influence of the American Revolution also introduced Indian nationalists to the idea that armed struggle could be a legitimate means of securing independence. Subhas Chandra Bose, who believed that peaceful protests alone would not be sufficient to overthrow British rule, was inspired by the revolutionary tactics used during the American Revolution. He formed the Indian National Army (INA) with the help of the Japanese during World War II in an attempt to liberate India through military action.
Bose’s views were controversial, but they reflected the revolutionary spirit of the American Revolution, where armed resistance was a key strategy for achieving independence. While Gandhi and others emphasized nonviolence, Bose and his supporters believed that force could sometimes be necessary in the face of British intransigence.
5. The Influence of the American Constitution
The U.S. Constitution, which was drafted in 1787, became another key inspiration for Indian nationalists. The American Constitution provided a blueprint for establishing a democratic government with checks and balances, individual rights, and a system of representation. Many Indian nationalists, particularly those who were educated in Western institutions, admired the American system of government and sought to replicate it in India.
Jawaharlal Nehru, who later became India’s first prime minister, was greatly influenced by Western democratic ideals, including those in the U.S. Constitution. Nehru and other leaders of the Indian National Congress envisioned an independent India governed by a democratic constitution that would guarantee civil rights and provide for political participation. The American model of democracy inspired many of the provisions of India’s own Constitution, which was adopted in 1950.
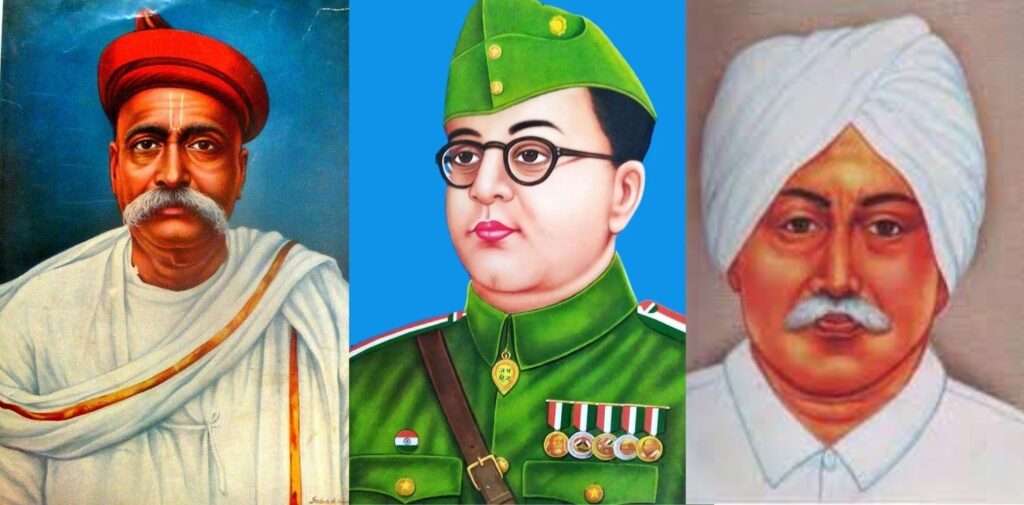

Key Indian Nationalists Influenced by the American Revolution
Several key Indian leaders were directly influenced by the American Revolution and its ideals. Here are a few notable examples:
- Bal Gangadhar Tilak: Tilak, one of the most important early leaders of the Indian nationalist movement, was deeply inspired by the American Revolution. He saw the struggle of the American colonists as a parallel to India’s own fight for freedom. Tilak’s famous slogan, “Swaraj is my birthright, and I will have it,” reflects the influence of the American demand for independence and self-rule.
- Subhas Chandra Bose: Bose admired the American Revolution for its use of armed struggle and was inspired by the revolutionary spirit it embodied. He believed that a strong, assertive resistance against the British was necessary for India’s freedom. Bose’s efforts to form the Indian National Army were directly influenced by the methods used in American and other global revolutions.
- Lala Lajpat Rai: Rai, a key figure in the freedom struggle, was another nationalist leader influenced by the American Revolution. He believed that India’s fight for independence was similar to the American struggle for liberty and often spoke about the need for Indians to fight for their rights.
Conclusion: Influence of the American Revolution
The American Revolution played an important role in shaping the thinking of Indian nationalists. The ideas of freedom, self-governance, equality, and popular sovereignty that were central to the American struggle for independence resonated strongly with Indian leaders and thinkers. These ideas provided the intellectual foundation for India’s own fight for freedom from British colonial rule.
While India’s path to independence was unique and involved nonviolent resistance and mass mobilization, the influence of the American Revolution can still be seen in the demands for democratic governance and the rights of individuals. The American Revolution gave Indian nationalists the hope and conviction that it was possible to overthrow a colonial power and create a nation based on justice, equality, and self-determination.
Thus, the American Revolution helped shape India’s journey to independence by inspiring a generation of leaders and thinkers who were determined to achieve the same rights and freedoms for their own country. The principles of the American Revolution continue to resonate in India’s democratic values and institutions to this day.