India has a long history of great kings, philosophers, and religions. One of the most important religions to have shaped India’s history is Buddhism. Founded by Siddhartha Gautama, who became known as the Buddha, Buddhism has had a lasting impact on the culture, philosophy, and society of India and the world. One of the key events in Buddhist history were the Buddhist Councils.
The Buddhist Councils were meetings held by the followers of Buddha to preserve his teachings and spread Buddhism further. These councils were important because they helped organize and clarify Buddha’s ideas. They also shaped the way Buddhism grew in India and beyond. In this article, we will learn about the different Buddhist Councils and their impact on Indian history.
What Were the Buddhist Councils?
A Buddhist Council was a gathering of monks and scholars who came together to discuss and preserve the teachings of Buddha. These councils were held after Buddha’s death to make sure that his ideas were passed on correctly and to prevent any confusion or mistakes in understanding his teachings. Over time, there were several councils, each playing a key role in spreading Buddhism and shaping its future.
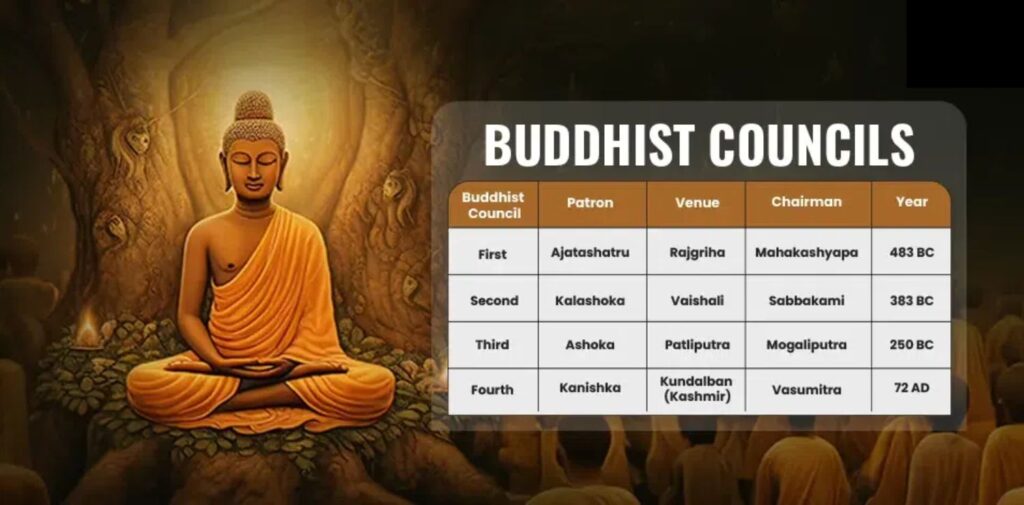
The First Buddhist Council
The first Buddhist Council was held soon after Buddha’s death, around 483 BCE. The meeting took place in Rajgir, a city in modern-day Bihar. After Buddha passed away, his followers wanted to preserve his teachings and the rules of the Buddhist community. The council was organized by Mahakasyapa, one of Buddha’s closest disciples.
At this council, 500 monks gathered to recite and agree on the teachings of Buddha. They wanted to make sure that there was no misunderstanding or change in his teachings. The Tripitaka, which is the collection of Buddha’s teachings, was compiled during this meeting. This collection contains three sections: the Sutra Pitaka (Buddha’s discourses), the Vinaya Pitaka (rules for the Buddhist community), and the Abhidhamma Pitaka (philosophical and doctrinal teachings). The first council was very important because it helped preserve the core of Buddha’s teachings for future generations.
The Second Buddhist Council
The second Buddhist Council took place around 100 years after Buddha’s death, around 383 BCE. This meeting was held in Vesali, a city in the northeastern part of India. By this time, the Buddhist community had grown, and there were disagreements about certain practices. Some monks started to follow rules that others thought were not in line with Buddha’s teachings. These disagreements led to the need for another council to settle the differences.
The second council was led by Mahadeva, and it was focused on resolving the conflict within the Buddhist community. It was decided that the monks who were following the incorrect practices should be expelled from the community. This council played a crucial role in ensuring that the original teachings of Buddha were followed properly and helped keep the Buddhist community united.

The Third Buddhist Council
The third Buddhist Council was held around 250 BCE during the reign of the great Indian Emperor Ashoka. Ashoka is one of the most famous rulers in Indian history, and he played a key role in spreading Buddhism across India and beyond. He became a follower of Buddhism after seeing the horrors of war and violence. The third council took place in Pataliputra (modern-day Patna), and it was led by the monk Mahinda.
At this council, the main focus was to purify the Buddhist teachings and separate them from the incorrect or corrupted practices that had crept into the community. The council also decided to send Buddhist missionaries to different parts of the world, including Sri Lanka, to spread the teachings of Buddha. This council helped Buddhism spread widely in Asia, and Ashoka’s support made it a state religion in India.
The Fourth Buddhist Council
The fourth Buddhist Council took place in Kashmir around the 1st century CE. This council was different from the others because it was held by two main groups of Buddhists: the Theravada and Mahayana schools. These two groups had some differences in how they interpreted Buddha’s teachings.
The Theravada Buddhists believed that they should stick closely to the original teachings of Buddha, while the Mahayana Buddhists were more open to new ideas and practices. The council was organized to address these differences and to discuss the future of Buddhism.
During this council, the Mahayana school became more prominent, and it spread its ideas to many parts of Asia, especially China, Korea, and Japan. The teachings of the Mahayana school included the idea that everyone could become a Buddha, not just the monks. This council played an important role in shaping the different branches of Buddhism that we see today.

The Impact of the Buddhist Councils on Indian History
The Buddhist Councils were extremely important in the development and spread of Buddhism. Here are some of the key impacts they had on Indian history:
- Preserving Buddha’s Teachings: One of the most important roles of the councils was to preserve and standardize Buddha’s teachings. They made sure that the original message of Buddhism was passed on correctly to future generations. Without these councils, there could have been confusion or distortion of Buddha’s teachings.
- Unity in the Buddhist Community: The councils helped settle disagreements within the Buddhist community. They helped unite monks from different parts of India and ensured that the core beliefs of Buddhism were followed by everyone. This unity was important for the growth and strength of Buddhism in India.
- Spread of Buddhism Across the World: The third Buddhist council, in particular, had a huge impact on the spread of Buddhism outside India. Emperor Ashoka sent missionaries to places like Sri Lanka, Central Asia, and Southeast Asia, which helped Buddhism grow in these regions. Today, Buddhism is practiced in many countries, and its roots can be traced back to India and the councils that preserved its teachings.
- Development of Different Schools of Buddhism: The councils helped shape the two major branches of Buddhism – Theravada and Mahayana. While Theravada focuses on following the original teachings of Buddha, Mahayana is more flexible and emphasizes the idea that anyone can achieve Buddhahood. These two schools of thought have influenced how Buddhism is practiced in different parts of the world.
- Influence on Indian Culture and Society: Buddhism had a significant impact on Indian culture, art, and philosophy. The councils helped ensure that Buddhist ideas, such as compassion, non-violence, and meditation, were integrated into Indian society. These values influenced the way people lived, and many kings and rulers adopted them to promote peace and harmony.
Conclusion: The Lasting Legacy of the Buddhist Councils
The Buddhist Councils were not just important events in the history of Buddhism; they played a crucial role in shaping Indian history and the history of many other countries. By preserving Buddha’s teachings, settling disagreements within the community, and spreading Buddhism across Asia, the councils helped create a legacy that still exists today.
Buddhism continues to be a major religion in many parts of the world, and the ideas discussed and decided upon during these councils continue to inspire millions of people. The councils helped shape a peaceful and thoughtful tradition that values compassion, mindfulness, and wisdom – values that are still important in today’s world.
The Buddhist Councils are a reminder of how important it is to preserve and share knowledge, and how the teachings of great thinkers like Buddha can continue to shape the world for generations to come.




